Process
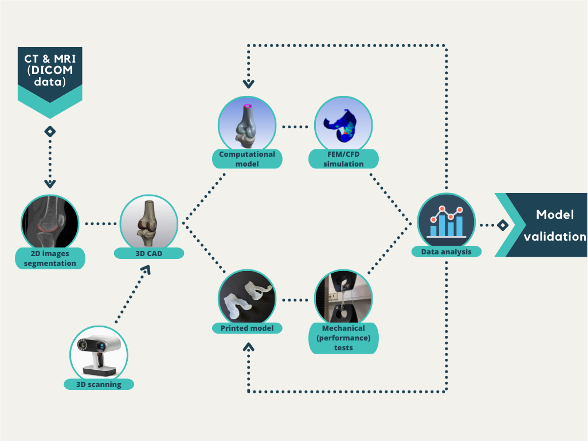
At the ICAAM - Icelandic Center for Advanced Additive Manufacturing the process starts with a CAD design or with DICOM or bitmap files which segmentations will be performed; alternatively, a 3D scanner can also be used to create a 3D model. In all cases, from the 3D model, we can study and simulate the mechanical characteristics and/or 3D printing. The computational model helps to predict the physical behaviour under specific conditions and thus, depending on the application, FEM or CFD analysis can be performed on it. The printed model is manufactured with the 3D printer that better fits the request (rigid, soft, transparent or opaque).
2D Images Segmentations
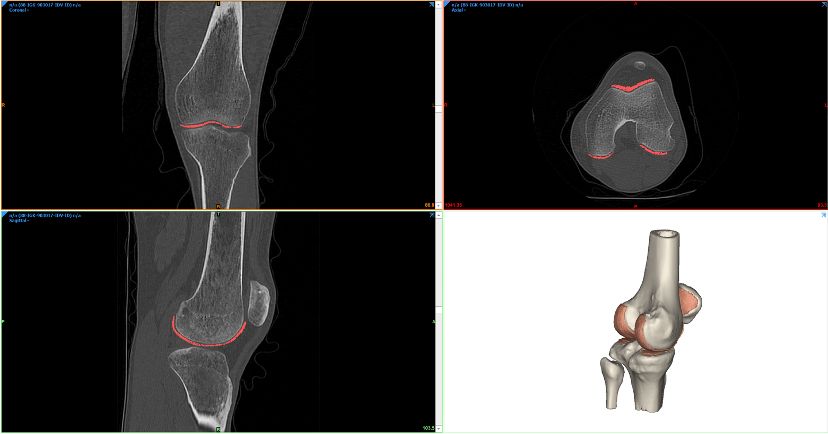
A software for medical image segmentation allows the user to visualize data from CT and/or MRI scans and highlight specific areas of interest for a following 3D segmentation.
3D Scanning

3D scanning is a technology for creating digital three-dimensional models based on the geometry of existing objects, ranging from the size of a gearbox to a vehicle
3D CAD
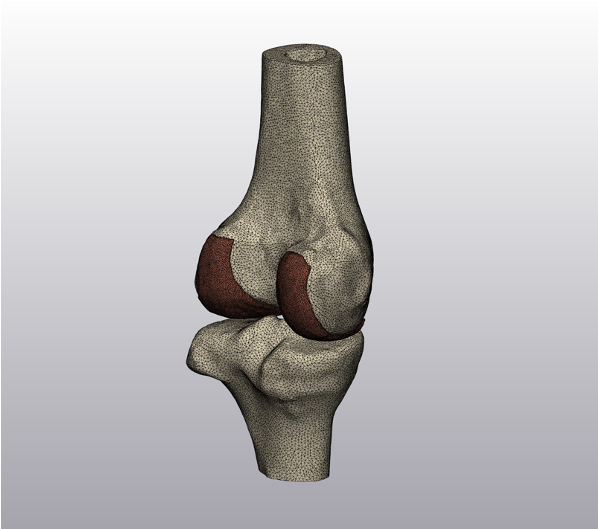 | 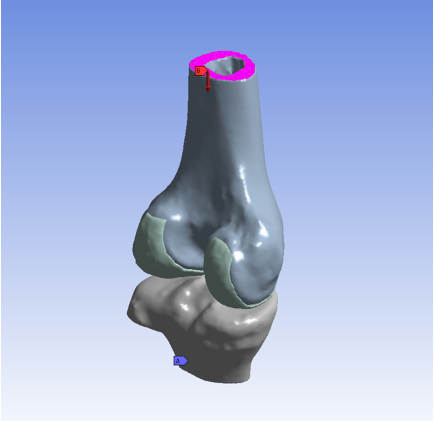 |
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software provides tools for the optimization of a 3D model, thus including the creation of surface and volume meshes, a requirement for Finite Element Analysis.
Computational Model Refers to the possibility of replicating specific boundary conditions (ex. fixed support) and loads (ex. force, pressure) on the designed geometry with a wide range of available analysis set-ups.
FEM/CFD Simulation
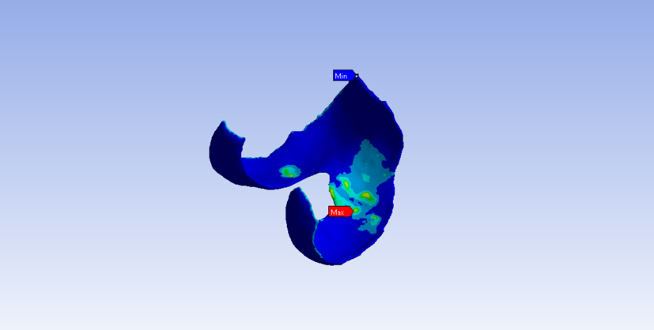 | 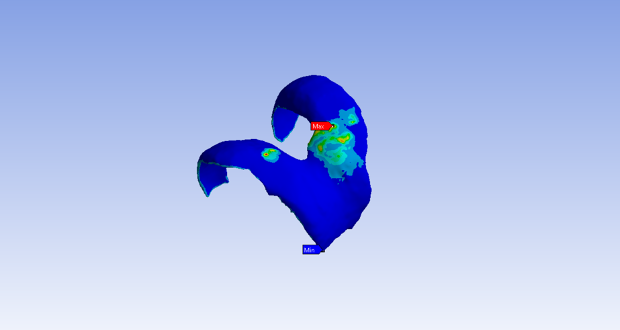 |
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) use calculations, models and simulations to predict and understand how a solid or fluid might behave under specific physical conditions.
Printed Model
 |  |
An anatomical printed model is the outcome of an innovative additive manufacturing workflow, which implies the use of different materials by combining them together to reproduce implants or anatomical parts for several types of applications (ex. surgical planning).
Mechanical Tests

Mechanical testing is used to determine the performances (thus, the properties) of a material under given mechanical strains and stresses.
Data Analysis

Data evaluation is based on the results from both the computational and the physical analysis, in order to compare them and find the right inputs (ex. material properties, loads) for validating the process.

