ICAAM
Icelandic Center for Advanced Additive Manufacturing (ICAAM)
The global industry is in the early stages of the transformation of product design, manufacturing, and service operations, enabled by additive manufacturing (AM) or 3D printing. In the coming years, this technology will be commonplace and change the way products are designed and manufactured. To join the AM industry and participate in this paradigm shift requires 3d printing infrastructure of various kinds and training and education of the workforce at different levels.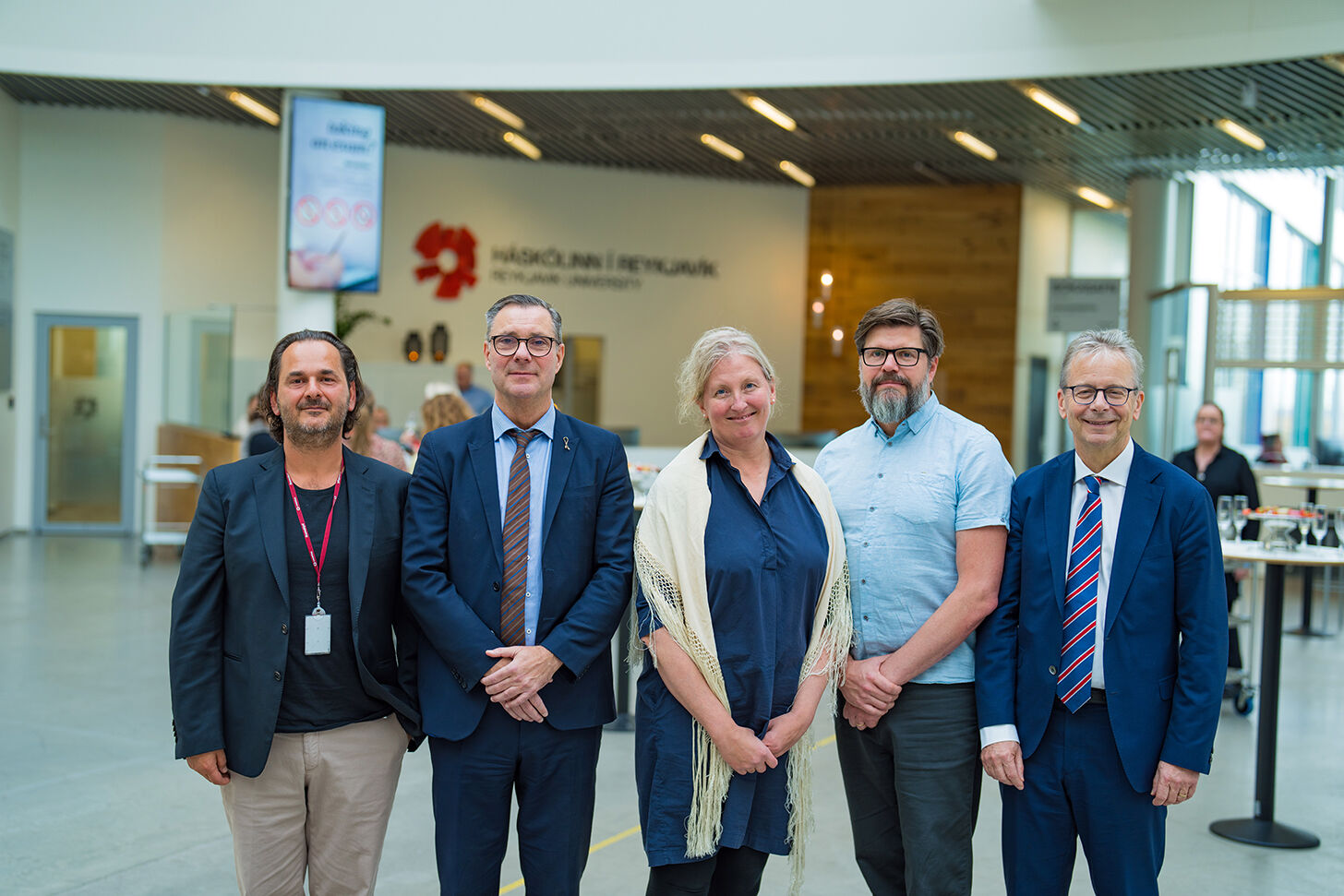 From left. Dr Paolo Gargiulo, Willum Þór Þórsson, Minister of Health, Dr Ragnhildur Helgadóttir President of Reykjavik University, Ágúst Valfells chair of Department of Engineering at RU & Dr Jón Atli Benediktsson President of the University of Iceland.
From left. Dr Paolo Gargiulo, Willum Þór Þórsson, Minister of Health, Dr Ragnhildur Helgadóttir President of Reykjavik University, Ágúst Valfells chair of Department of Engineering at RU & Dr Jón Atli Benediktsson President of the University of Iceland.
Partners

ICAAM is a part of the 2022 roadmap for infrastructure in materials science and materials engineering. RANNIS infrastructure fund. This infrastructure is a collaborative effort between, Reykjavik University, The University of Iceland, Össur, Landspítalinn, Marel, Iceland University of Arts and Tæknisetur.
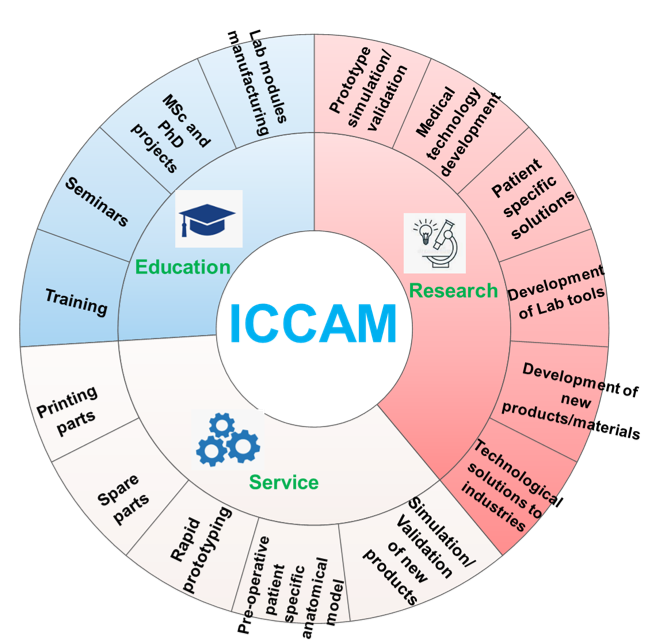
The ICAAM research facility is an initiative of the Institute of Biomedical and Neural Engineering to establish multidisciplinary infrastructure to advance health care in Iceland.
This lab will enable cutting-edge research and development in numerous fields including materials science and engineering, advanced manufacturing, 3d modelling and product optimisation. It will bring research and development capabilities up to high international standards. Cutting-edge research in these fields has been shown to be the basis for advanced technology development and the high-tech industry.
The main aims of ICAAM are to enable advanced surgical planning, build complex anatomies, research and product development for the Icelandic industries such as high technology, medical, food processing equipment, construction, film and art, and geothermal power technology.
For example, the printer will be used to:
- Develop anatomical prototypes such as vascular structures and cardiac models for the simulation of surgical and clinical procedures.
- Create functional prototypes in various industries.
- Rapid manufacture of specialised tools.
- Manufacture multi-material, multicolour parts.
- Educate and train students at the university level allowing them to explore the possibilities opened by this technology.